
DSCI 554 lecture 12
Study guide
Dr. Luciano Nocera

Final examination
Format:
- MCQ similar to Quizzes
- On content from lectures
- 60 MCQ questions in 4 parts
- When: FRIDAY, DECEMBER 10, 2-4 P.M.
Data and information visualization
- Uses of data visualization
- Infovis vs. scivis
- Affordances and signifiers
- Big data units (kilo-, mega-, giga-, tera-, peta-, exa-, zetta-, yotta- byte)
- Designer encodes information, User decodes information
- Information used by designers:
- Forms adapted to nature of information
- User familiarity with form
- User knowledge of topic
- User abilities
- Display type and size
- Context where the form is used
- Guidelines for choosing visualization forms:
- Form constrained by the goals of the visualization
- Form follows function
- Visualizations are means to achieve goals
- Visualizations are devices that help an audience complete certain tasks
- DIKW pyramid
- Data: numerical, interval, ratio, categorical, nominal, ordinal, dichotomous
- Named graphs and maps: scatterplot, scatterplot matrix (grid of scatter plots used to visualize bivariate relationships between combinations of variables), stripchart (1d scatterplot), bubble chart, bar chart, lollipop chart, coxcomb chart (stacked bar chart with radial layout), Marimekko chart (bar chart where the width encodes relative size, also called Mekko chart), waterfall chart, pie chart (stacked bar charts in polar coordinates, angle encodes proportion), donut chart, line chart, sparkline, slopegraph, parallel coordinates, radar chart (graphical method of displaying multivariate data in the form of a two-dimensional chart of three or more quantitative variables represented on axes starting from the same point, also called web, spider, star, cobweb, polar, or Kiviat chart), area chart, streamgraph (tacked area graph displaced around a central axis), dendrogram, Reingold–Tilford tree (hierarchical data as linked tree layout implemented using the Reingold-Tilford algorithm), treemap (hierarchical data as nested rectangles, area proportional to value), sunburst (hierarchical data as rings. center is root node. angles are equal or proportional to value), alluvial diagram (relations between multivariate data), sankey diagram (magnitude of flow between
- nodes in a network), network graph (relationships as lines between entities as nodes), heat map (matrix values as colors), chord diagram (shows directed relationships among a group of entities in a matrix), word cloud, bubble cloud, circle packing (bubble cloud technique with hierarchical information as enclosing circles), time series plot (values ordered in time as a line chart), index chart (interactive line chart that shows percentage changes for a collection of time-series based on a selected index point), gantt chart (schedule with tasks layed out on time axis), timeline (events layed out on time axis), thematic maps (choropleth, proportional symbol map, dot map (can be used to locate each occurrence of a phenomenon, one-to-one or one-to-many), cartogram, isopleth), choropleth (areas are shaded or patterned in proportion to variable), proportional symbol map (scaled symbols show data for areas/locations, also called graduated symbol map), dot map, cartogram (area used to display value, distortion used to show continuous variables), isopleth or isarithmic (use contours to show continuous variables), topographic map (detailed quantitative representation of land relief using contour lines), nautical map (charts of maritime/coastal area), image based map (using satellite or aerial imagery), combo or combination chart (combination of multiple charts, can have multiple series and y-axes).
- Statistical graphics: boxplot (shows quartiles, distribution skewness, tails, outliers in unimodal distributions) also named box-and-whisker plot), violin plot (mirrored probability density), dot plot (statistical chart consisting of data points plotted on a fairly simple scale, typically using filled in circles), frequency distribution table (displays the frequency of various outcomes in a sample, also called frequency table), population pyramid or age-sex pyramid (graphical illustration of the distribution of a population by age groups and sex), stem-and-leaf plot (device for presenting quantitative data in a graphical format, similar to a histogram, to assist in visualizing the shape of a distribution), histogram (approximate representation of the distribution of numerical data), frequency polygon (histogram as a line chart), Q–Q or quantile-quantile plot (graphical method for comparing two probability distributions by plotting their quantiles against each other), Heatmap of Pearson’s correlation coefficients (graphical tool to assess correlations in multivariate data), scree plot (line plot of the eigenvalues of factors or principal components in an analysis), biplot (generalization of the simple two-variable scatterplot with variables displayed either as vectors, linear axes or nonlinear trajectories)
- Graphical elements in charts: title, legend, axes, axes labels, labels grid lines, tick marks, tick labels
- Infographic: graphic visual representations of information, data or knowledge intended to present information quickly and clearly, Receiver Operator or ROC Curve(diagnostic tool for binary classifiers with decision threshold),
- Dashboard: graphical user interface which often provides at-a-glance views of key performance indicators (KPIs) relevant to a particular objective or business process.
Visual system information processing
- Eye: fovea, retina cones (S, M, L), rods distribution, blind spot
- Visible spectrum: 400-700nm
- Highest visual resolution in central 1~2 degrees of the fovea
- Visual system comprised of eyes, nerves and the visual cortex (V1-5)
- Bottom-up and top-down processing
- Saccades, fixations
- Selective attentional tuning: when presented with superposed layers, we can focus on one layer
- Priming
- Inattentional blindness: failure to detect an unexpected stimulus that is fully visible due to limited attention
- Change blindness: failure to detect a brief transitory event occurring in the visual field, when we blink, iconic memory
- Pre-attentive processing: no attention, from a single glimpse, works on large displays
- Pre-attentive tasks: target, boundary and region detection, counting and estimation
- Pre-attentive feature hierarchy: how certain preattentive features are easier to detect than others
- Target and distractors
- Conjunction search: search involving a combination of non-unique features
- Basic visual preattentive properties: color, orientation, size, motion, stereoscopic depth
- Pop-out effect: universal property, independent of practice, familiarity with the features and number of distractors
- The greater the distance between target and distractors the greater the pop-out effect
- Visual pathways (two stream hypothesis): Works without visual input,
- Where / Dorsal visual pathway: relative object location for motor tasks
- What / Ventral visual pathway: object identification and recognition
- Pattern recognition: process that matches information from a stimulus with information retrieved from memory
- Priming: Effect in which exposure to one stimulus influences a response to a later stimulus.
- Apophenia: Perception of images or sounds in random stimuli, priming increases likelihood of seeing the pattern
- Convergence: group of cells form a receptive field for a cell in the brain
- Neuronal tuning: Simpler tuning in earlier visual areas (V1 & V2), Complex tuning in higher visual areas (V4 & IT)
- Lower visual cortex: low information, high localization, universal experience, pop-out, developed early, e.g., V1 neurons may fire to any vertical stimulus.
- Higher visual cortex: high information, low localization, individual experience, no pop-out effect, e.g., IT neurons may fire only to a specific face.
- Some neurons of V1 are tuned to vertical lines, others to diagonal lines
- Memory types: Iconic, VSTM, VLTM, from visual persistance to information persistance
- Iconic memory: Unlimited capacity, Retention: ≤ 1s, high bandwidth, works unconsciously, provides temporal integration ensures continuity during saccades
- VSTM memory: Limited capacity, Retention: ≤ 30s, Buffer that stores temporary information, Constructs and manipulate visual images
- VLTM memory: Large capacity, Retention: indefinite, Capacity increases over childhood, declines with old age, Encodes information semantically for long term storage, Subject to fading, recalls help preserve it
Color and perception
- Chromatic aberration effect: red/blue perceived at different distance
- Types of color scales: sequential, divergent, qualitative
- Primary and secondary colors
- After-images and predicting colors using additive RGB color model
- Color properties distinguishable: Hue, Saturation, Brightness
- Color vision theories working together: trichromatic (R, G, B cones) and opponent process (visual system responds to opponent channels R-G, B-Y, B-W)
- Trichromatic theory problems: no R-G or Y-B, R-G overlap, small B response, afterimages)
- Subtractive color model: print, Primaries: CMY, secondary: RGB
- Additive color model: computer screens, Primaries: CMY, secondary: RGB
- Additive color displays: addition of illumination (projectors), partitive mixing (LCD), time mixing (OLED), binocular mixing (stereovision)
- Color model: abstract mathematical model describing the way colors can be represented as tuples
- RGB, HSV color models
- Color blindness: about 9% of the population, R-G
Color and perception
- False colors techniques: choropleth, density slicing (divides the image into few colors)
- Pseudocolor, e.g., colored IR image
- Simultaneous color contrast: colors of different objects affect each other
- Color constancy: ensures color remain relatively constant under varying illumination
- Mach bands: illusion due to simultaneous contrast - can appear in color scales
- Sharpening: More sensitive to dark than light differences, affected by background
Depth and perception
- Perceptual egocentric space: up, towards, sideways
- Oculomotor depth cues: accommodation, convergence, myosis
- Visual depth cues: binocular (stereopsis), monocular (static, motion-based)
- Classic pictorial (static) depth cues: Occlusions, Linear perspective convergence, Relative/Familiar size, Texture gradient, Shadows, Shading, Defocus blur, Atmospheric perspective
- Motion-based depth cues: Motion parallax, Occlusion in motion (deletion, accretion), Structure from motion
- Simultaneous size contrast
- Size constancy
- Ponzo illusion (size constancy), Muller-Lyer illusion, Necker cube
Maps and GIS
- Thematic maps: choropleth, proportional symbol map, cartogram, dot map, isopleth, dasymetric map
- Geographic coordinates: latitude longitude in degrees
- Geodetic datum: coordinate system and reference ellipsoid to locate places
- Horizontal datum: defined by reference ellipsoid
- Vertical datum: used to measure elevation, can be Geodetic, Tidal, Gravimetric
- Geocentric datum: good for global applications
- Local datum: good for regional applications
- Properties preserved in maps: conformal (shape), Equal-area (area), Equidistant (point distance), Azimuthal (direction from a point)
- Cannot have maps that are both conformal and equal-area
- Developable surfaces used for map projections: Cylindrical, Conical, Azimuthal (plane)
- Map projection can be: Tangent or Secant, Normal, Transverse or Oblique
- Common projections: Albers conic, Lambert azimuthal equal-area, Lambert conformal conic, Mercator projection, Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM)
- Composite projections: same projection optimized for different areas, e.g., Albers USA
- Mercator projection: standard for Web mapping applications
- Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) projection is a projection over over $61 \times 6^o$ zones in cartesian coordinates, no trigonometry is needed to compute distances, units in meters as Easting and Northing
- Maps in the Browser can be raster (images) or vector (SVG)
- Tile Map Service (TMS): e.g., Google maps serve map tiles also called slippy maps
- GeoJSON: JSON map format defining Geometry (Point, LineString, Polygon, MultiPoint, MultiLineString, MultiPolygon, GeometryCollection), Feature and FeatureCollection
- TopoJSON: GeoJSON extension where to encode topology (Geometry is indexed with
arcs
) leading to smaller files - GeoJSON and TopoJSON coordinates can be in geographical or projected coordinates
Visual design
- Visualization wheel dimensions (Abstraction-Figuration, Functionality-Decoration, Density-Lightness, Multidimensionality-Unidimensionality, Originality-Familiarity, Novelty-Redundance)
- Visualization wheel dimensions more intelligible and shallower vs. more complex and deeper
- Cairo's design principles (clarify, seek depth, add boom effect)
- Cairo's suggestion to deal with novel forms (use redundancy)
- Minimalistic visualizations
- Tufte principles: 1. Above all else show data, 2. Maximize the data-ink ratio, 3. Erase non-data-ink, 4. Erase redundant data-ink, 5. Revise and edit
- Nigel Holmes design principle: Use humor to instill affection in readers for numbers and charts
- Data-ink ratio (Data-ink / Total ink used to print the graphic, Proportion of a graphic’s ink devoted to the non-redundant display of data-information, 1.0−Proportion of a graphic that can be erased without loss of data-information)
- Chartjunk
- Visual query: a pattern cognitively specified, that if found in the display will contribute to the solution of a problem
- Ware design principles: Carefully craft visualizations to optimize visual queries, leverage information that the brain processes efficiently, (e.g., pre-attentive features) to prioritize most important information
- Avoid attentional overload and change blindness
- Uses of colors (Tufte): Label (identify, highlight, group), measure, represent or imitate reality, enliven or decorate
- Color design guidelines:
- blue text hard to read (fewer blue cones)
- achromatic (BW) channel is easier to read (use all 3 cones)
- colors harder to read (achromatic ~ 3 x chromatic channel info)
- W on B less strain than B on W
- Be considerate of colorblind people
- Respect well-established color sequences
- Shape from shading is recognized from the luminance channel
- Observe cultural conventions
- Use consistent aesthetics
- Most important visual queries should have most weight
- Apprehandable chunk: unlearned pattern complexity that can be apprehended in one fixation
- Apprehendable chunks consist of about three components
- Sketches are less work to understand than images.
- Gestalt principles: Emergence, Reification, Multi-stability, Invariance
- Gestalt laws of grouping: Proximity, Similarity, Closure, Continuity, Common fate, Connection, Common region
- Gestalt is useful in graphics and UI
- Semiology: visual language is a sign language, sender encodes information in signs and receiver decodes information from signs.
- Visual variables: marks (points, lines, areas...) and encodings/channels (position, size, value, texture, color, orientation, shape)
- Accuracy of perceptual tasks, e.g., points more accurate than area than color
- Isotype: International System Of TYpographic Picture Education (Neurath)
- Miller's law: The Magical Number Seven, Plus or Minus Two (1-D information judgment task)
- LSTM capacity 4-5 items with characters
- LSTM capacity 3-4 items with basic visual features & interference task
- Multiple graphs usually better than single graphs: Faceting, conditioning, latticing, trellising, small multiples
- Ways to deal with overplotting: transparency, outline shape, jitter, summarize, add information (e.g., regression line), split (small multiples)
Statistics
- Population and sample
- Descriptive vs. inferential statistics
- Independent and dependent variables vs. features, labels
- Measures of order
- Quantiles and quartiles definitions
- Measures of central tendency
- Distribution modes, skewness and tails
- Frequency & Relative frequency
- Graphic forms adapted to descriptive statistics for univariate and multivariate data
- Boxplot: quartiles and whiskers $Q1 - 1.5 \times IQR$, $Q3 + 1.5 \times IQR$
- Steam-and-leaf plots and how to build
- Histogram and how to build
- Visualizing model performance: confusion matrix, reporting accuracy, precision, recall, and F-1 scores as tables
Visualization software
- Nomenclature: Chart Typologies, Visual Analysis Grammars, Visualization Grammars, Component Architectures, Graphics applications
- Expressiveness vs. ease-of-use of tools (Heer14 table)
- General knowledge of various tools: Google Sheets, Matplotlib, Seaborn, VizQL, Tableau, ggplot2, plotnine, Altair, Protovis, D3, Vega, Vega-Lite, Prefuse, Flare, Improvise, VTK, Processing, P5.js, WebGL, Three.js, OpenGL
- Grammar of graphics: graphic defined as a "grammar" of "components"
- HTML basic elements
- HTML global (id, class, style) and element specific attributes
- inline vs. block-level HTML elements
- CSS classes, ids, selectors
- CSS pseudo-classes for handling events, e.g.,
#bar:hover - CSS inheritance
- Ways to include CSS and javascript in pages (inline, embedded, external)
- Javascript (user interaction, asynchronous communications, control the browser, alter content)
- Javascript features (oo, first class functions, dynamic typing, block-level scope)
- Javascript basics and closures
- SVG basic shapes and attributes (rect, circle, ellipse, line, polyline, polygon)
- SVG attributes defaults (position and size is 0, fill is black, stroke is none)
- SVG path and it's uses in visualization
- SVG transformations, e.g.. translate, rotate
- AJAX
- DOM box model
- DOM event models (DOM Level 0: inline and traditional, and DOM Level 2)
- DOM level 2 event bubbling (default) and capturing phases
- D3 features: javascript library, declarative syntax
- D3 what it is and what it does:
- Loads data in the browser (DOES NOT HIDE THE DATA!)
- Binds data to document elements
- Transforms elements by interpreting each element’s bound datum and setting its visual properties
- Transitions elements between states in response to user input
- Basic d3 operations (implemented with function chaining):
- Select elements
- Add new elements to selected elements
- Delete selected elements
- Modify selected elements to position and style
- D3 default data join maps data according to corresponding data and selection order
- D3 data join with keys syntax: updates can occur anywhere in the data array, depending on the overlap between the old and new values.
- D3 general update pattern basic order:
data join, update, enter, enter + update, exit - D3 margin convention and how to use
- D3 select/append mechanism
- D3 axes
- D3 scales domain range
- D3 scale Continuos and Ordinal
- D3 scales useful for colors: Linear, Sequential, Diverging, Quantize, Quantile, Threshold, Ordinal
- Computing and recognizing basic scales (scaleLinear, scalePoint, scaleBand, scaleTime...)
- D3 data format (js array [] of objects)
- D3 loading json vs. csv, tsv
- D3 layouts and generators general knowledge
- D3 maps in GeoJSON or TopoJSON, data join by Feature and d3.geoPath() used to transform Feature to <path>
- D3 event listeners implement DOM Level 2 event model .on(), calling a listener function
- D3 transition: only one transition at the time per element
- D3 transition events: start, end, interrupt
- D3 array methods .min, .max, .ascending, .descending
- js library vs. framework: you call library code in your code, framework code calls your code
- Dataframes: table where columns are variables, rows are observations, string variables can be stored as factors
- Recognize dataframes proper form
- Basics Jupyter & Pandas: ?, help('list'), import, read_csv, describe
- Layered Grammar of Graphics derived from Wilkinson's Grammar of graphics
- Layered Grammar of Graphics components: Defaults (Data and Mapping), Layer (Data, Mapping, Geom, Stat, Position, Scale), Coord, Facet
- ggplot2: implementation of the Layered Grammar of Graphics
- Minimal ggplot2 plot: Data, Aesthetic Mapping, Geom
- ggplot2 minimalistic plot:
- ggplot2 aes() is used to reference variables in data (dataframe)
- ggplot2 basic named plots: geom_point(), geom_text(), geom_bar(), geom_line(), geom_area(), geom_dotplot(), geom_histogram(), geom_freqpoly(), geom_grammar(), geom_violin()
- ggplot2 faceting, e.g., facet_grid(rows = vars(var1), cols = vars(var2)), facet_grid(var1 ~ var2), facet_wrap(var1)
- Tableau: built on VizQL an implementation of Grammar of graphics where mappings are specified interactively and visually
- Dimensions (categorical) and Measures (numerical) variables in Tableau
- SVG vs. canvas elements
- canvas API: used with 2D context (
getContext('2d'), shape, text image rendering functions - canvas with WebGL: used with 3D context (
getContext('webgl')) primitives: GL_POINTS, GL_LINES, GL_LINE_STRIP, GL_LINE_LOOP, GL_TRIANGLES, GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP, GL_TRIANGLE_FAN - In WebGL and related toolkits data is passed as indexed arrays
- Graphic pipeline: process of rendering a 3D scene in WebGL, includes vertex shader, triangle assembly, rasterization, fragment shader, testing and blending, steps
- Model and view matrices: used in WebGL to place the object to render and the camera in a world coordinate system
- Projection matrix: used to define how 3D is projected in the camera, can be defined using the clipping planes
- Three.js: High-level access to WebGL and graphical utilities, e.g., scene, camera, model loaders, lights and materials
- Processing: simplified Java API for drawing and graphics
- Processing.js: JS API to use Processing code
- P5.js: HTML5 processing implementation
- Deck.gl and Mapbox GL JS 3d rendering capabilities
Notes
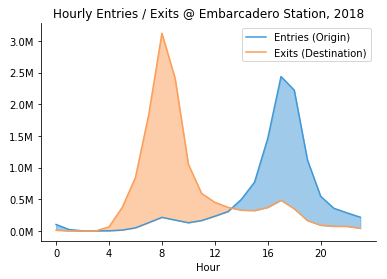
- Stripline
- Slopegraph
- Line chart
- Area chart$\leftarrow$
div, p a.foo {
color: red;
font-weight: bold;
}
- div elements, hyperlinks with class foo and paragraphs
- div elements, hyperlinks with class foo in paragraphs $\leftarrow$
- div elements, paragraphs in hyperlinks with class foo
- div elements in paragraphs or in hyperlinks with class foo
<svg style="height: 25px; background-color: lightpink;">
<rect x="20" y="5" width="100" height="10" fill="blue"></rect>
<text x="0" y="20" style="font-size: 0.65em">5</text>
</svg>
- $\leftarrow$
<!-- assume data.csv contains:
Color
Red
Green
Blue
-->
<p>Orange</p>
<script>
d3.csv("data.csv").then(function(data) {
d3.select("body")
.selectAll("p")
.data(data)
.enter()
.append("p")
.text(function(d) {return d.Color; })
});
</script>
- Orange, Color, Red, Green, Blue on separate lines
- Orange, Green, Blue on separate lines$\leftarrow$
- Color, Red, Green, Blue on separate lines
- Red, Green, Blue on separate lines
- Basic features that pop-out correspond to the basic visual patterns processed by the brain
- Pop-out is an individual property
- In feature space, the smaller the distance between target and distractors the smaller the pop-out effect
- The pop-put effect depends on practice, familiarity and number of distractors
Answer: A and C
- By adding a key to the data-join, updates can occur anywhere in the data array.
- If a key is not specified, then the first datum in values is assigned to the first element in the selection and so on.
- Is usually implemented by formatting the data as an array of objects with some key-value property for the keys.
- Is realized by specifying the keys in the second argument in selection.data(values, [, key])
Answer: A, B, C and D
73 42 67 78 99 84 91 82 86 122
A. The decimal point is 1 digit(s) to the right of the | C. The decimal point is 1 digit(s) to the right of the |
4 | 2 4 | 2
6 | 738 6 | 837
8 | 24619 8 | 91642
10 | 10 |
12 | 2 12 | 2
B. The decimal point is 1 digit(s) to the right of the | D. The decimal point is 2 digit(s) to the right of the |
4 | 2 0 | 4
5 | 0 | 7788899
6 | 7 1 | 02
7 | 38
8 | 246
9 | 19
10 |
11 |
12 | 2
Sorted values: 42 67 73 78 82 84 86 91 99 122
Answer: A, B and D
10 1 0.1 7.5 8.8 2 3.5 6.7
A. The decimal point is at the | C. The decimal point is at the |
0 | 10 0 | 1
2 | 05 1 | 0
4 | 2 | 0
6 | 75 3 | 5
8 | 8 4 |
10 | 0 5 |
6 | 7
7 | 5
8 | 8
9 |
10 | 0
B. The decimal point is at the | D. The decimal point is 1 digit(s) to the right of the |
0 | 01 0 | 0124
2 | 50 0 | 789
4 | 1 | 0
6 | 57
8 | 8
10 | 0
Sorted values: 0.1 1.0 2.0 3.5 6.7 7.5 8.8 10.0
Answer: A, C and D